Table of Contents
While many sales leaders and entrepreneurs focus on one approach over the other, understanding when and how to use both inbound and outbound strategies can be the key to sustainable growth. The hybrid method allows businesses to benefit from both worlds—capturing inbound leads while actively pursuing outbound opportunities to fill the pipeline.
This guide will break down:
- The key differences between inbound vs outbound sales.
- When to use each approach for maximum impact.
- Actionable sales development strategies to enhance your lead generation.
- Common pitfalls in B2B sales development and how to avoid them.
Whether you’re optimizing your sales team or starting from scratch, this guide will help you make informed decisions that fuel business growth.
Understanding the Fundamentals
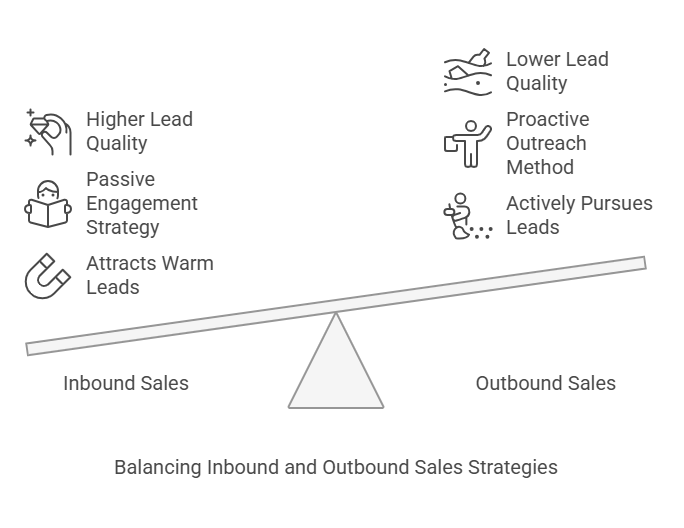
Inbound Sales: A Value-Driven Approach
Inbound sales revolve around attracting customers by offering valuable content that resonates with their needs. Unlike outbound tactics, which involve directly reaching out to prospects, inbound marketing builds relationships by providing solutions that align with potential buyers’ pain points.
Core Inbound Sales Strategies:
- Content Marketing:
The foundation of inbound sales lies in producing high-quality content that speaks directly to your target audience’s challenges. This type of content can include blog posts, downloadable resources, webinars, and case studies that provide practical insights and solutions. Through consistent content production, inbound sales attract prospects who actively seek information related to your product or service.
Example: A SaaS company could publish a detailed guide like “How to Choose the Right CRM System for Your Business,” offering valuable insights and showing potential customers how their CRM solution can solve a variety of business challenges.
- SEO and Keyword Strategy:
For inbound sales to succeed, it’s crucial that your content is easily discoverable. Optimizing your website and content for SEO ensures you can reach customers who are actively searching for information relevant to your business.
Tip: Start by researching sales development strategies keywords—target terms that align with the intent of your audience. Use tools like SEMrush, Ahrefs, or Google Keyword Planner to find long-tail keywords and optimize your content. By implementing technical SEO, your site can rank higher, bringing in organic leads that already have an interest in your product.
- Lead Nurturing:
Once visitors land on your website, the next step is nurturing these leads through personalized engagement. Through email automation and retargeting campaigns, you can keep your brand top of mind. Automated workflows can segment leads based on their interests, sending them targeted content that aligns with where they are in the buying journey.
Example: For a lead who downloaded a case study on improving sales processes, you could send them an email sequence with more in-depth product demos and customer success stories.
Studies show that companies with established inbound strategies typically experience a 3x higher conversion rate compared to outbound-only approaches, underscoring the importance of a well-thought-out inbound strategy. It’s not just about generating traffic; it’s about converting visitors into qualified leads by providing the information they need when they need it.
Outbound Sales: A Proactive and Direct Approach
Outbound sales development, on the other hand, involves proactively reaching out to potential customers. Outbound sales techniques require targeting specific individuals or accounts and engaging them directly, often through emails, phone calls, or social selling.
Outbound can be especially effective when you’re targeting a specific group of prospects or when you need to scale your efforts quickly. It’s a faster approach compared to the longer-term inbound sales process.
Key Outbound Sales Strategies:
- Targeted Cold Outreach:
The key to successful cold outreach is personalization. By understanding the specific pain points of your prospects, you can craft highly tailored emails or messages that speak directly to their needs. This method requires research on the potential customer, such as their industry, business size, and challenges, to make the outreach relevant and compelling.
- Example: If your company offers digital marketing services, you could reach out to a small business owner by mentioning their website’s recent redesign and how you can help improve their online traffic with SEO and content marketing strategies.
- Account-Based Marketing (ABM):
Account-based marketing is a targeted approach where sales and marketing teams collaborate to focus on specific high-value accounts. ABM involves crafting customized outreach campaigns to address the individual needs of each account, often across multiple touchpoints.
Tip: Use technographic targeting to identify accounts that might benefit most from your offering based on their current software stack. For instance, if you’re selling a project management tool, focus on companies using inefficient project management software that could benefit from your solution.

- Social Selling:
Platforms like LinkedIn allow sales reps to interact with decision-makers in a non-intrusive way. By engaging in meaningful conversations and sharing valuable insights through posts and comments, you can build relationships before initiating a direct outreach.
Example: Start by commenting on a prospect’s LinkedIn post with thoughtful insight, and then send a message that ties into the conversation you’ve already started.
Outbound sales development requires consistency, but when done right, it delivers fast results and helps generate predictable pipelines. It’s especially effective when targeting decision-makers at companies with a clear need for your solution.
Inbound vs Outbound Sales: Key Differences
Factor Inbound Sales Outbound Sales
Lead Quality Higher intent, lower volume Lower intent, higher volume
Sales Cycle 3-6 months nurturing typical 30-90 days common
Team Structure Content creators, SEO specialists SDRs, sales enablement tools
Cost Structure Higher initial, lower over time Consistent operational costs
Best Use Cases Complex solutions, enterprise sales. Transactional sales, niche markets
When to Use Each Approach
- Inbound sales work best when you’re targeting a market that requires education and time for decision-making. It’s ideal for businesses offering more complex solutions or services that involve a longer research phase, such as B2B sales development for SaaS, consulting, or enterprise solutions.
- Outbound sales are more effective when targeting a specific list of prospects and focusing on immediate needs. For example, selling simple products with clear value propositions, like a tool to improve internal communication or a specialized marketing service, benefits from a quick, direct sales cycle.
Advanced Implementation Strategies
Building an Effective Inbound Engine
- Content Strategy Development:
The content you produce should align with where your leads are in their buying journey. Develop a content map that targets the right stage—whether it’s awareness, consideration, or decision.
Example: Early-stage content should address general challenges or industry trends, like “The Future of Digital Marketing.” Later-stage content, however, might include case studies or product demos, such as “How Company X Increased Leads by 25% with Our Solution.”
- Lead Scoring Model:
Once you’ve attracted visitors to your site, you need a lead scoring model to identify which leads are most likely to convert. Implement a system that factors in both demographic data (e.g., job title, company size) and behavioral data (e.g., downloaded resources, time spent on key pages).
Tip: Consider using a predictive lead scoring model, powered by AI, to ensure you’re focusing your efforts on leads who are most likely to convert.
- Conversion Optimization:
Optimizing your website’s landing pages is crucial for converting leads. Test different versions of your forms, CTAs, and offers to see what resonates most with your audience.
Example: For a service-based business, you might create a landing page that speaks to potential leads with a pain point, such as “Struggling with lead generation? Learn how we can help you close more deals.”
Optimizing Outbound Performance
- List Building Best Practices:
Build a well-defined list of leads by researching the ideal customers for your product or service. Use intent data signals to identify prospects who are showing signs of interest in your industry.
Example: If you’re selling a marketing tool, find prospects who have been actively searching for digital marketing services or software.
- Outreach Sequencing:
Once you have your list, it’s time to develop a sequence of outreach attempts. A good practice is to send 5-7 emails or messages over 2-3 weeks. Spread these across multiple channels like email, phone calls, and social media.
Tip: Include value-added content in your follow-up emails, such as blog posts, case studies, or whitepapers, to increase the likelihood of engagement.
- Conversation Intelligence:
Use conversation intelligence tools to track how prospects are responding to your outreach. These tools help analyze call recordings and email responses, offering insights on improving your messaging for better outcomes.
Example: If you’re getting more responses from a specific segment (e.g., prospects from a particular industry), tailor your next outreach efforts to focus more on that segment.
Hybrid Sales Approach: Combining Inbound and Outbound
The hybrid approach integrates both inbound and outbound sales development to leverage the strengths of each strategy. This method ensures a more consistent lead flow, faster conversions, and higher-quality leads.
- Integrate Content with Outreach:
Use inbound content to support your outbound efforts. For example, if you reach out to a prospect, provide them with a relevant blog post or case study that offers additional value.
Tip: Create a content library that your sales team can use for outreach. This enables your reps to quickly share relevant, helpful content that aligns with the prospect’s needs.
- Lead Recycling Process:
If an outbound lead isn’t ready to buy, nurture them with inbound content over time. Likewise, leads from your inbound efforts that go cold can be re-engaged using outbound outreach.
Example: If a prospect downloaded a whitepaper and hasn’t responded to follow-up emails, consider using an outbound method like a phone call or a personalized LinkedIn message to reconnect.
Final Recommendations
By combining inbound and outbound strategies, you create a more effective sales development process. The key to success lies in maintaining alignment between both teams.
Hybrid Mindset:
Inbound and outbound are not competing methods—they complement each other. Inbound works best for building trust and educating prospects, while outbound helps generate immediate leads. Together, they create a full-funnel sales process.
- Actionable Tip: Use inbound content, like blog posts or case studies, to nurture leads from outbound outreach.
Team Collaboration:
Collaboration between sales and marketing is essential. Both teams must share common goals and work closely together to ensure smooth handoffs and data sharing.
- Actionable Tip: Hold regular alignment meetings to ensure both teams are on the same page regarding lead quality and KPIs.
System Integration:
Integrate your inbound and outbound efforts into a unified CRM system. This ensures leads are tracked, nurtured, and followed up on without manual intervention.
- Actionable Tip: Implement automated workflows in your CRM to track and nurture leads seamlessly from both inbound and outbound efforts.
Implementation Roadmap:
- Months 1-3: Set up your CRM and develop buyer personas and content. Launch small outbound campaigns to identify target accounts.
- Months 4-6: Scale your efforts with Account-Based Marketing (ABM) and refine your inbound content based on performance data.
- Month 7+: Optimize your sales engine based on the insights gathered and scale your hybrid strategy.
Key Integration Tactics:
- Repurpose Content: Use inbound content like whitepapers or case studies in your outbound emails.
- Retargeting: Retarget those leads with inbound ads or follow-ups after an outbound conversation.
- Account-Based Nurturing: Implement account-based nurturing to keep high-value leads engaged.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ’s)
Start with a 70:30 split, favoring inbound, especially if you’re in the early stages. As your efforts mature, you may shift to a more balanced 50:50 or 60:40 ratio depending on the performance data.
Inbound: Focus on a content team, SEO specialists, and a marketing ops team.
Outbound: Build a strong SDR team (Sales Development Representatives) and provide them with sales enablement tools to enhance productivity. Both teams should work together under a revenue operations framework.
Inbound: Focus on Marketing Qualified Leads (MQLs), content engagement, and traffic.
Outbound: Measure meetings booked, opportunities created, and the conversion rate from outbound interactions.
Shared Metrics: Ultimately, both teams should contribute to the same goal of increasing pipeline revenue.
Yes, startups often begin with outbound strategies for quick results. However, as they scale, building inbound assets—like SEO-driven content—becomes essential for long-term growth.






